
Thermal insulation of wood
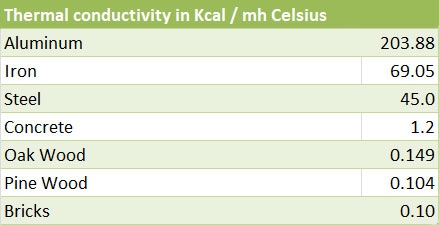
The most suitable material, in terms of thermal insulation, for the manufacture of window frames is wood. Compared to metals, the thermal insulation capacity of wood is 4,000 times greater than steel and 1,800 times the thermal insulation capacity of aluminum.
An example of the thermal insulation offered by wood is that for centuries now it is used as a handle for hot objects and vessels.
For these reasons, wood was and remains the preferred material for the manufacture of window frames in particularly cold areas such as Scandinavia, the Republics of the former Soviet Union and, more generally, the countries of Northern Europe.
Second place in the thermal insulation occupies the plastic frame and lastly the aluminum frame, which as an excellent heat conductor.
The aluminum frame, commonly used in Greece, not only fails to act heat-insulatingly, but acts as a heat-shrinking, essentially ‘storing’ the cold or heat inside it, thereby increasing the cost of controlling the temperature of an interior space.
It is clear, therefore, that the use of wooden frames in a building automatically reduces the energy consumption it will need to warm up in the winter or to cool in the summer.
Additionally, the advanced technological materials used in the production of a modern wooden frame such as double thermal insulating glazing and joint sealing means further increase the thermal insulation properties of the frames thus creating an excellent result.
Sound insulation of wood
The wood has very good sound-proofing properties that the other materials do not have.
Because of its porous structure, it contains in its mass a sufficient amount of space, each of which traps the sound and reduces reverberation.
This makes it a unique material for use in a bedroom, considering the city noise and the need for peace and tranquility that we all want to have when we return home.
Nowadays, special soundproof doors are manufactured in the form of a single-layered construction with successive layers, with a sound-insulating core interference between two wooden blankets that minimize noise.
With regard to the manufacture of double-glazed windows or multiple-pane windows or inert gas, high-profile curtains and glass-fiber composite glass and intermediate acoustic films are used in the manufacture of wooden frames and significantly increase their sound-proofing capability.
Source: Hoyle, R.J. 1975. Physical Character of Wood in Wood Structures (pp. 1-31). American Society Civil Engineers ASCE, N.Y.
