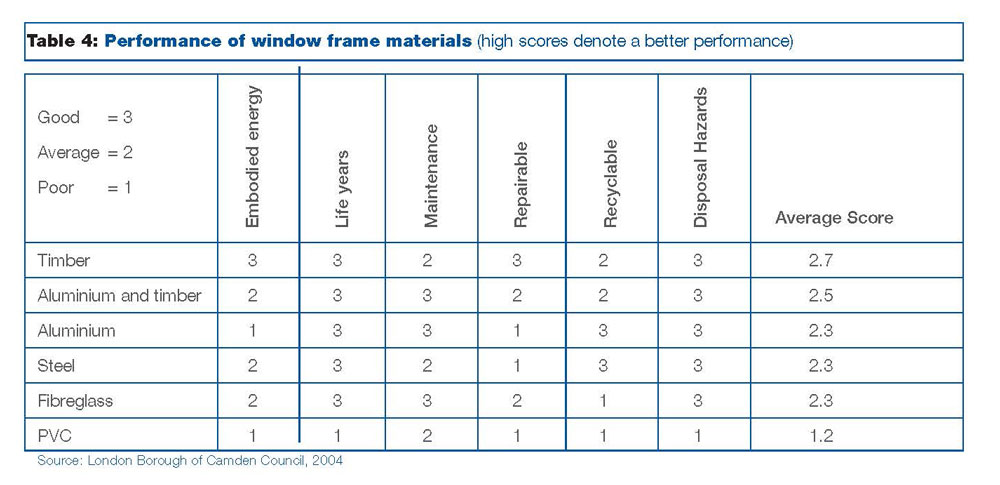
Wood differs from other materials. According to published data from international organizations such as WWF, wood and, as a result, products from it, the environment burden is minimal and therefore deserves the first place in choosing the most eco-friendly material.
In order to understand the superiority of wooden frames in terms of the low energy consumption required for their production, it is enough to see the production procedure followed for the two main competitors: PVC and aluminum.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride or vinyl) is a thermoplastic material based on petroleum and chlorine and is a widely used synthetic material.
WWF’s international environmental organization estimates that for every window made of PVC, a total of 49.9 kilograms of carbon dioxide (CO2), 84% of raw material production and 16% of window frames are released.
On the contrary, the production of a wooden frame of the same type and size in total releases only 5.7 kg of CO2. However, PVC also creates environmental problems throughout its life cycle, with the most important release of highly toxic substances (carcinogenic dioxins, HCl, heavy metals, etc.) during combustion, which usually takes place after removal from use.
On the other hand, we also encounter similar problems in the manufacture of aluminum. Dangerous pollutants are released during production while large amounts of CO2 are released during the production of the very large amounts of energy needed to isolate the material from its raw materials.
At the same time, according to a study by the US Department of Energy, carbon monoxide (CO), especially PFCs, are released in the aluminum production process.
The latter are 6,500 times more damaging to the greenhouse effect than CO2. Wood is the only material that not only does not burden the environment but also has a negative carbon dioxide emission indicator when it is produced as it encases CO2 in its growth as a tree.
See also WWF 2005 publication
Source of information: xylinokoufoma.pdf

